Climate change is one of the most discussed and debated topics in the world today. It’s a complex issue that affects everyone, everywhere, and understanding the science behind it is crucial for making informed decisions about our future. This blog will explore what climate change is, the science that explains it, and the impact it has on our planet and our lives.
What Is Climate Change?
Climate change refers to significant, long-term changes in global climate patterns. While the Earth’s climate has always fluctuated, the term “climate change” today usually refers to the recent trend of global warming, driven primarily by human activities. This warming is leading to changes in weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems across the globe.
The key driver of this change is the increase in greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O), trap heat in the atmosphere, creating a “greenhouse effect” that warms the planet. While this effect is natural and necessary to keep the Earth warm enough to sustain life, human activities have significantly increased the concentration of these gases, leading to more heat being trapped and, consequently, global warming.

The Science of Climate Change
The science of climate change is based on decades of research and data collected by scientists around the world. The primary evidence for climate change includes:
- Rising Global Temperatures: The Earth’s average surface temperature has increased by about 1.2°C (2.2°F) since the late 19th century, with most of the warming occurring in the past 40 years. This is largely due to the increase in greenhouse gases.

- Melting Ice Caps and Glaciers: The polar ice caps and glaciers around the world are melting at an unprecedented rate. This not only contributes to rising sea levels but also disrupts ecosystems and wildlife that depend on cold environments.

- Rising Sea Levels: Sea levels have risen by about 8 inches (20 cm) since the late 19th century, primarily due to the melting of ice and the expansion of seawater as it warms. This poses a significant threat to coastal communities around the world.

- Changes in Weather Patterns: Climate change is leading to more extreme and unpredictable weather events, including heatwaves, hurricanes, floods, and droughts. These changes have far-reaching impacts on agriculture, water supply, and human health.

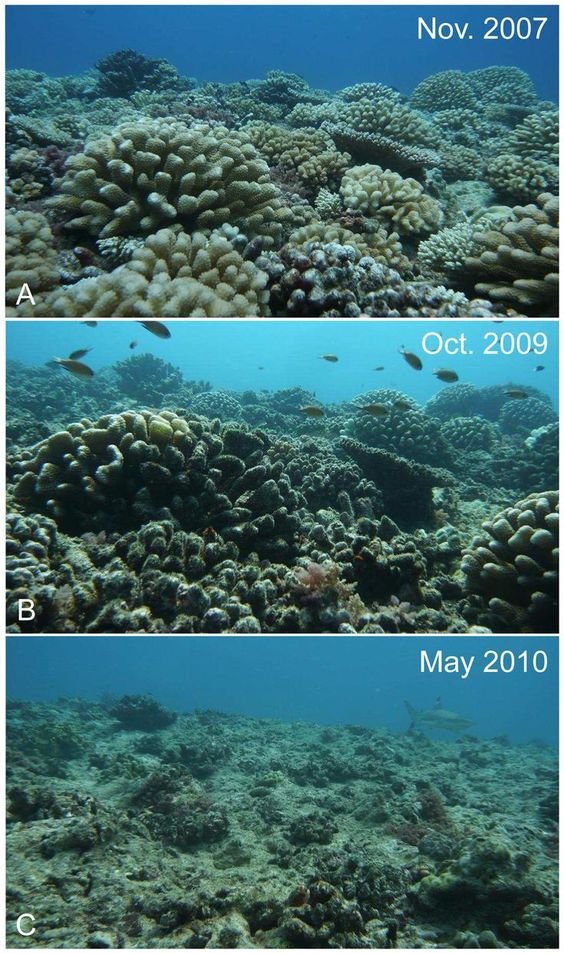
- Ocean Acidification: The oceans absorb about 30% of the CO₂ released into the atmosphere. This process leads to ocean acidification, which negatively affects marine life, particularly organisms with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons, such as corals and shellfish.
The Impact of Climate Change
The impacts of climate change are widespread and multifaceted, affecting ecosystems, economies, and communities around the world. Some of the most significant impacts include:
- Threats to Biodiversity: As temperatures rise and habitats change, many species are at risk of extinction. For example, polar bears rely on sea ice to hunt, and as the ice melts, their survival is threatened. Similarly, coral reefs, which are home to a vast array of marine life, are dying due to warmer and more acidic ocean waters.

- Health Risks: Climate change poses direct and indirect health risks. Heatwaves can lead to heatstroke and dehydration, while changing weather patterns can increase the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue fever. Additionally, air pollution, exacerbated by climate change, can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular problems.

- Economic Impacts: The economic costs of climate change are immense. Natural disasters, such as hurricanes and floods, cause billions of dollars in damage. Moreover, changes in weather patterns can affect agriculture, leading to food shortages and increased prices. Climate change also impacts tourism, especially in regions that rely on natural beauty, such as coral reefs or ski resorts.

- Social and Political Tensions: As resources like water and arable land become scarcer due to climate change, competition for these resources can lead to social unrest and conflict. Additionally, climate change can lead to displacement, creating climate refugees who are forced to leave their homes due to rising sea levels or extreme weather events.

What Can Be Done?
Addressing climate change requires a global effort. Governments, businesses, and individuals all have a role to play in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to the changes that are already occurring. Here are some key actions:
- Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions: This can be achieved by transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydropower, and improving energy efficiency in homes, buildings, and transportation.
- Protect and Restore Ecosystems: Forests, wetlands, and oceans act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO₂ from the atmosphere. Protecting these ecosystems and restoring degraded ones can help mitigate climate change.
- Adaptation Strategies: Communities need to adapt to the changes that are already happening. This includes building flood defenses, developing drought-resistant crops, and planning for the relocation of communities at risk from rising sea levels.
- International Cooperation: Climate change is a global problem that requires international cooperation. Agreements like the Paris Agreement, where countries commit to reducing their emissions, are essential for making progress on a global scale.

Conclusion
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time, and understanding the science behind it is crucial for addressing it effectively. While the challenges are significant, there are also opportunities to create a more sustainable and resilient future. By taking action now, we can mitigate the worst impacts of climate change and protect the planet for future generations.

